Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral infection that has become a public health concern due to recent outbreaks. Understanding its symptoms, transmission methods, and effective prevention strategies is essential for individuals seeking to protect themselves and their communities. This article provides valuable insights into recognizing mpox symptoms, how the virus spreads, and the necessary steps to take following a diagnosis.
By equipping yourself with knowledge about mpox, you can enhance your ability to prevent infection, seek appropriate medical care, and contribute to public health efforts. Whether you are looking for guidance on treatment options or practical prevention measures, this article aims to address your needs with clear and actionable information.
In this article you will find:
Understanding Mpox Symptoms and Transmission
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, has emerged as a significant public health concern, particularly in light of recent outbreaks. Understanding the symptoms and transmission methods associated with this viral infection is crucial for effective prevention and management. This section delves into the distinctive signs of mpox and how the virus spreads, empowering readers with the knowledge they need to protect themselves and others.
Recognizing Mpox Symptoms
Mpox symptoms can vary in severity and may appear between 5 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. Recognizing these signs early can facilitate timely medical intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: Often the first sign, accompanied by chills and fatigue.
- Headache: Severe headaches may occur, often signaling the onset of the illness.
- Muscle Aches: General body aches and pains are common.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: This distinguishes mpox from similar diseases like smallpox.
- Rash: A characteristic rash develops, starting as flat lesions and progressing to raised bumps, which eventually form scabs.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Coughing and sore throat may also occur in some cases.
It is important to note that while mpox can be mistaken for other illnesses, the combination of swollen lymph nodes and the specific rash pattern can help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis.
How Mpox Spreads
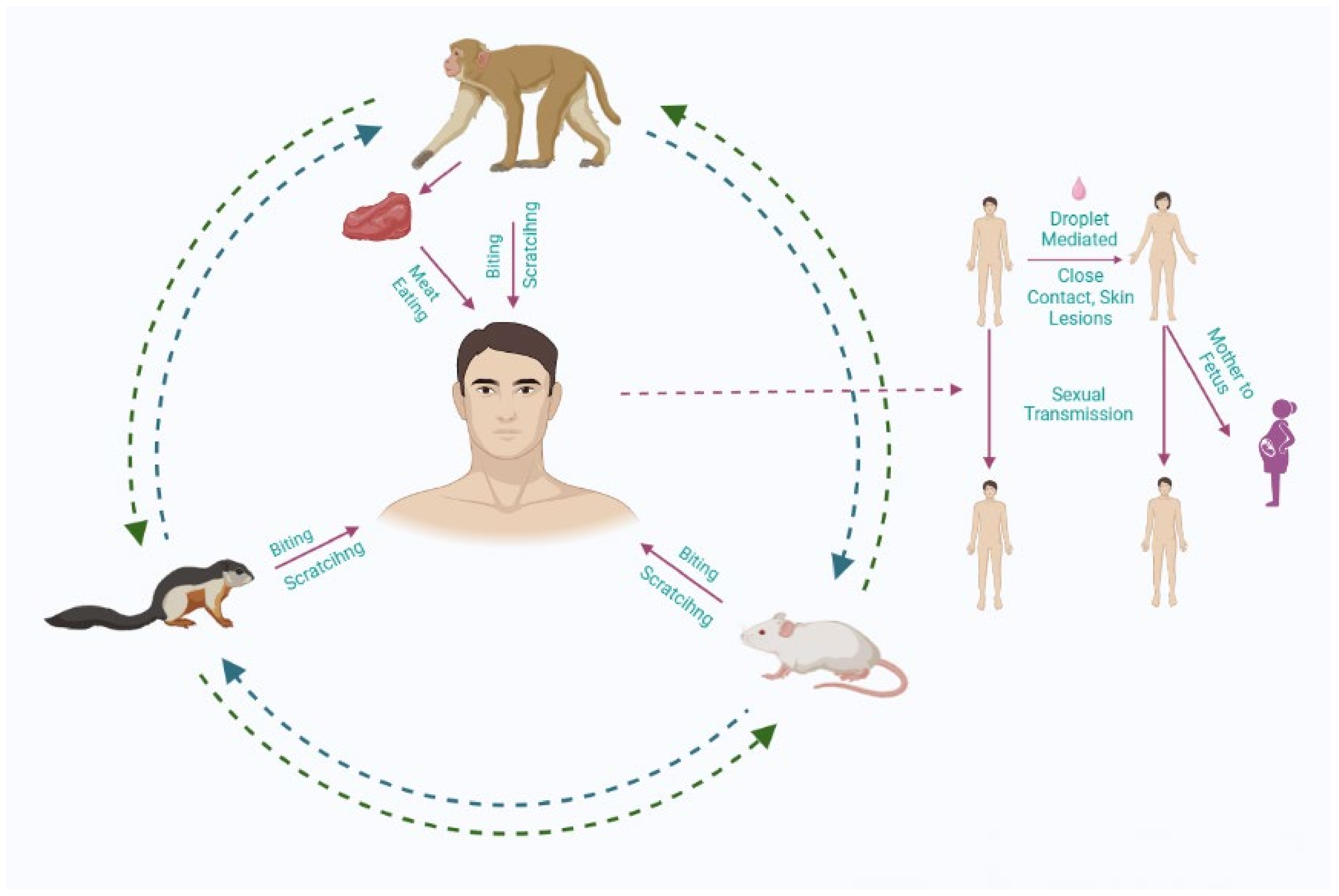
The transmission of mpox primarily occurs through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, lesions, or respiratory droplets. Understanding these transmission methods is vital for implementing effective preventive measures. Key modes of transmission include:
- Direct Contact: Touching the skin lesions or bodily fluids of an infected person can lead to transmission.
- Respiratory Droplets: Prolonged face-to-face contact may allow the virus to spread through respiratory droplets, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Contaminated Objects: Items such as bedding, clothing, or utensils that have come into contact with an infected person can harbor the virus.
- Animal Contact: Mpox can also be transmitted from animals to humans, particularly through bites or scratches from infected animals.
Given these transmission routes, it is crucial for individuals to practice good hygiene and take precautions, especially when in close contact with those who may be infected.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of mpox symptoms not only aids in effective treatment but also helps to curb the spread of the virus. If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms consistent with mpox, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Health professionals can provide guidance on testing, isolation, and treatment options.
For more detailed information on mpox and its implications, consider visiting the CDC’s Mpox page, which offers comprehensive resources on prevention, symptoms, and treatment guidelines.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Mpox
Preventing mpox is essential for safeguarding individual and public health, especially in light of recent outbreaks. By understanding and implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of infection. This section outlines practical measures that can be adopted to prevent the spread of mpox.
Practice Good Hygiene
Maintaining proper hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of mpox. Consider the following hygiene practices:
- Regular Handwashing: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces or individuals.
- Use Hand Sanitizer: In situations where soap and water are unavailable, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Refrain from touching your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands to minimize the risk of introducing the virus into your body.
Avoid Close Contact
Minimizing close contact with individuals who exhibit symptoms of mpox is crucial for prevention. Here are some guidelines:
- Maintain Physical Distance: Keep a safe distance from individuals who are symptomatic or have been diagnosed with mpox.
- Limit Group Gatherings: Avoid large gatherings, particularly in enclosed spaces where the virus can spread more easily through respiratory droplets.
- Wear Masks: In high-risk environments or when caring for someone with mpox, wearing a mask can help reduce the risk of respiratory transmission.
Vaccination and Medical Precautions
Vaccination is a critical tool in preventing mpox. While there is no specific vaccine for mpox, vaccines used for smallpox may provide some level of protection. Consider the following:
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Speak with your healthcare provider about the potential benefits of vaccination, particularly if you are in a high-risk group.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of vaccination programs and recommendations from local health authorities regarding mpox.
Educate Yourself and Others
Education plays a vital role in prevention. Understanding mpox and its transmission can empower individuals to take proactive measures. To enhance your knowledge:
- Follow Reputable Sources: Stay updated with information from trusted health organizations, such as the World Health Organization, which provides accurate and timely information about mpox.
- Share Knowledge: Educate friends and family about mpox symptoms, transmission methods, and preventive measures to foster a more informed community.
By adopting these prevention strategies, individuals can significantly contribute to reducing the spread of mpox. The next section will explore the current treatment options available for those who may be infected, ensuring that individuals are prepared to seek appropriate care.
Current Treatment Options and Guidelines
As mpox cases continue to be reported, understanding the treatment options available is crucial for those affected. While mpox is generally a self-limiting disease, timely medical intervention can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. This section provides an overview of the current treatment options and guidelines for managing mpox effectively.
Symptomatic Treatment
For most patients, mpox can be managed with symptomatic treatment. This approach focuses on relieving symptoms rather than targeting the virus directly. Key strategies include:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate fever, headaches, and body aches.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential, particularly if fever is present. Drinking fluids can help maintain hydration levels and support recovery.
- Skin Care: For those with rashes, keeping the affected areas clean and dry can prevent secondary infections. Topical treatments may also be recommended to soothe irritation.
Antiviral Treatments
In more severe cases, especially among high-risk populations, antiviral treatments may be considered. The following options are under investigation or have been used in clinical settings:
- Tecovirimat (TPOXX): Originally developed for smallpox, this antiviral medication has shown promise in treating mpox. It works by inhibiting the viral replication process.
- Cidofovir: This antiviral has been used in some cases of mpox, particularly for patients who are immunocompromised. It targets viral DNA synthesis.
- Brincidofovir: Similar to cidofovir, brincidofovir is being studied for its efficacy against mpox and may be used in specific clinical scenarios.
Guidelines for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a vital role in managing mpox cases. The following guidelines can assist in ensuring appropriate care:
- Isolation Protocols: Patients diagnosed with mpox should be isolated to prevent the spread of the virus, particularly in healthcare settings.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Regularly assess the patient’s symptoms and overall health to identify any worsening conditions that may require more intensive treatment.
- Referral to Specialists: In cases of severe disease or complications, referrals to infectious disease specialists may be necessary for tailored treatment plans.
Vaccination as a Preventive Measure
While the primary focus of this section is on treatment, it’s important to mention that vaccination can play a key role in preventing severe disease. Vaccines used for smallpox may provide cross-protection against mpox. Consult with healthcare professionals regarding vaccination opportunities, especially for those in high-risk categories.
For further details on treatment guidelines and emerging research related to mpox, consider visiting the CDC’s Mpox Treatment page, which offers up-to-date information and resources for healthcare providers.
Next Steps After Mpox Infection: What to Do
Receiving a diagnosis of mpox can be overwhelming, but understanding the next steps is vital for effective recovery and preventing further transmission. This section outlines essential actions to take after being infected with mpox, including care strategies, monitoring symptoms, and when to seek further medical assistance.
Follow Medical Advice
After being diagnosed with mpox, it’s crucial to adhere to the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider. This may include:
- Medications: Take any prescribed antiviral medications and pain relievers as directed to manage symptoms effectively.
- Regular Check-ups: Attend follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and address any complications that may arise.
Self-Isolation Guidelines
To prevent the spread of mpox to others, it is essential to follow self-isolation guidelines:
- Stay Home: Remain in isolation until your healthcare provider advises that you are no longer contagious, which is typically after all lesions have healed and scabs have fallen off.
- Avoid Close Contact: Limit interactions with household members, pets, and others to minimize the risk of transmission.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintain strict hygiene protocols, including frequent handwashing and sanitizing surfaces to reduce the risk of spreading the virus within your home.
Monitor Your Symptoms
Keeping a close eye on your symptoms is crucial for managing your health effectively. Key symptoms to monitor include:
- Fever and Body Aches: Note any increases in fever or worsening body aches, as these may indicate complications.
- Rash Progression: Track the development of any rashes or lesions, ensuring they are healing as expected.
- Breathing Difficulties: Be alert for any respiratory issues, which may necessitate immediate medical attention.
Emotional and Mental Well-being
Dealing with mpox can be stressful, and it’s essential to care for your emotional and mental health during recovery. Consider the following:
- Seek Support: Reach out to friends, family, or support groups to discuss your feelings and experiences.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in mindfulness, meditation, or gentle exercises to alleviate stress and anxiety.
Know When to Seek Help
It’s important to know when to contact your healthcare provider for further assistance. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe Symptoms: Increased fever, severe headaches, or respiratory distress should prompt immediate medical care.
- Signs of Secondary Infection: If lesions become increasingly painful, red, or show signs of pus, consult your doctor.
For more detailed guidance on managing recovery from mpox and resources for support, consider visiting the CDC’s Mpox Recovery page, which provides helpful information for those recovering from mpox. Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral infection characterized by symptoms such as fever, headaches, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, and a distinctive rash. It spreads primarily through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, contaminated objects, and animal bites. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further transmission.
To prevent mpox, individuals should practice good hygiene, maintain physical distance from symptomatic individuals, and consider vaccination where applicable. If infected, it is essential to follow medical advice, engage in self-isolation until cleared by a healthcare provider, and monitor symptoms closely. Emotional support and relaxation techniques can aid in recovery, while knowing when to seek further medical assistance is vital for managing complications. For more detailed information, resources from the CDC provide valuable guidance on mpox management.